Esophageal |
|
|---|---|
|
In gastroenterology, physicians using OCT may be able to diagnose esophageal cancer and Barrett’s esophagus earlier, giving patients a better chance to beat these devastating diseases. Laser implications: In esophageal OCT applications, the catheter can be positioned against the esophageal wall and must image both the near side and the far sides. The long working distance requirement necessitates a source with a long coherence length. The Insight laser provides a coherence length of 40 mm—many times longer than competitive light sources. High scan speed of the Insight laser allows faster imaging and less patient discomfort. The laser's high optical quality provides more faithful image segmentation, allowing more sensitive and specific diagnosis of precancerous conditions. Additional general information:
Additional technical information:
|
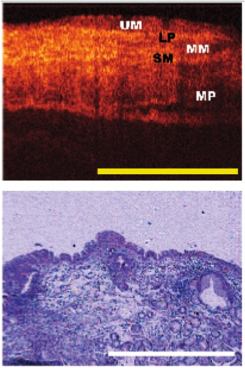
Barrett's esophagus OCT image (top)
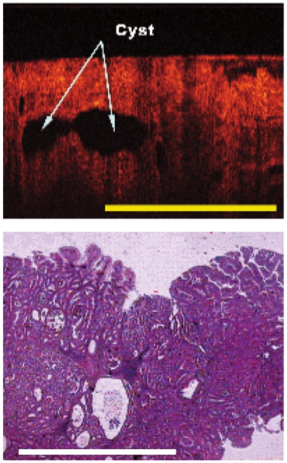
Cysts are clearly shown in the OCT scan (top image)
|
|
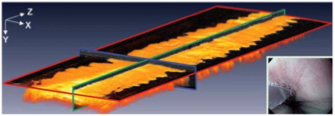
3D OCT image of normal esophageal tissue. |
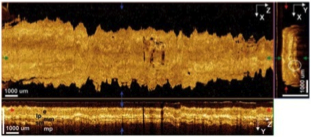
Abnormal esophageal and tumorous segment. |